How Mender works
Mender supports secure and robust updates, including firmware, operating systems, applications, and systems of devices. While alternatives and homegrown, bespoke update solutions exist, they fail to deliver the security, safety, scalability, and risk management enterprise OEMs require.
Learn how leveraging a purpose-built, enterprise over-the-air (OTA) update solution delivers unmatched device updating, troubleshooting, and monitoring securely and safely.
Mender Architecture
Mender is an open-core Apache 2.0-licensed solution, offering a streamlined version published on GitHub. A Mender plan offers advanced functionality, commercial features, enterprise-grade security, and expert support. Depending on the plan, Mender can be deployed to the cloud (private or public) or on-premises and managed by the Mender team or self-managed.
For all Mender deployments, the general Mender architecture comprises two main components: the Mender Server and the Mender Client on the device.
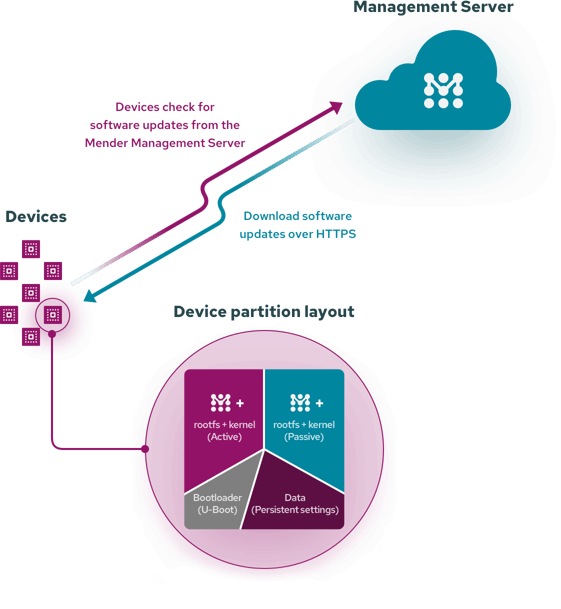
The Mender Server
The Mender Server stores and controls the deployment of software updates to your devices over-the-air. No costly site visits or physical intervention required!
Manage devices, upload and manage software releases, and create deployments to update device fleets using the Mender Server web-based interface or APIs.
The Mender Client
Running on the device, the Mender Client periodically reports to the Mender Server to check for updates; if a software update is available for that specific device, the client downloads and installs the update. The entire deployment is done securely, with encryption and cryptography from end-to-end and HTTPS polling. Devices remain secure, with no open ports.
Operating system updates: Relying on a fail-safe strategy
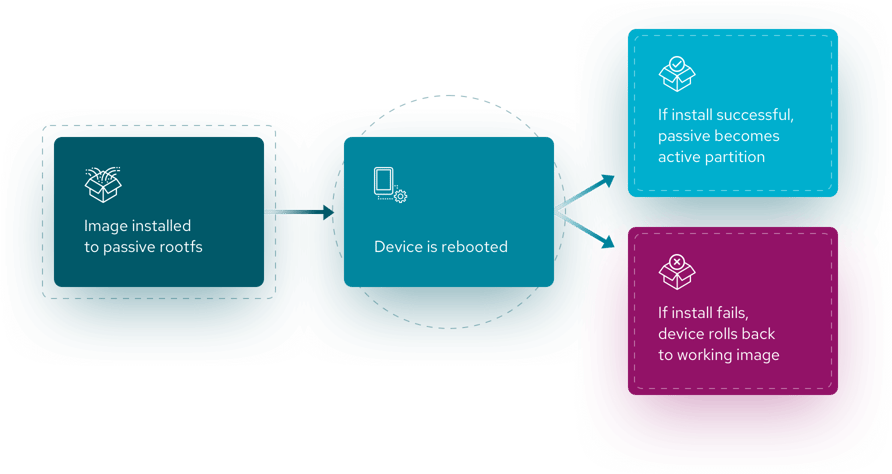
For operating system updates, Mender requires a dual A/B root file system (rootfs) partition layout on the device. A dual device partition strategy ensures that the device is always operable. The device can recover if the update deployment is incomplete or corrupted during installation for any reason, such as a loss of power or connectivity during the update process.
The Mender Client daemon runs in the currently booted (active) root file system (rootfs) partition – Partition A. During the update process, the Mender Client writes the updated image to the unused (inactive) root file system (rootfs) partition – Partition B – and configures the device to boot from the updated partition (Partition B). Once the update process is complete, the device reboots.
If the boot succeeds, Mender sets the updated partition (Partition B) to boot permanently when Mender starts as part of the boot process. If the boot fails for any reason, Mender automatically boots the unchanged partition (Partition A) instead.
By readily making an operable version available, Mender's dual A/B partitioning strategy ensures the device remains available and does not get bricked.
Other applications on the device continue to run as usual, even while Mender downloads and installs the image. The data partition stores persistent data, which is left unchanged during the update process. The only downtime the device experiences is rebooting, which typically requires around 60 seconds, depending on the configuration.
Update types: Leveraging unmatched flexibility
The Mender Client can support different types of updates, using an Update Modules framework. Update Modules give complete control and customizability over the installation of a software type. As independent executables, Update Modules support any software packaging format and installation approach.
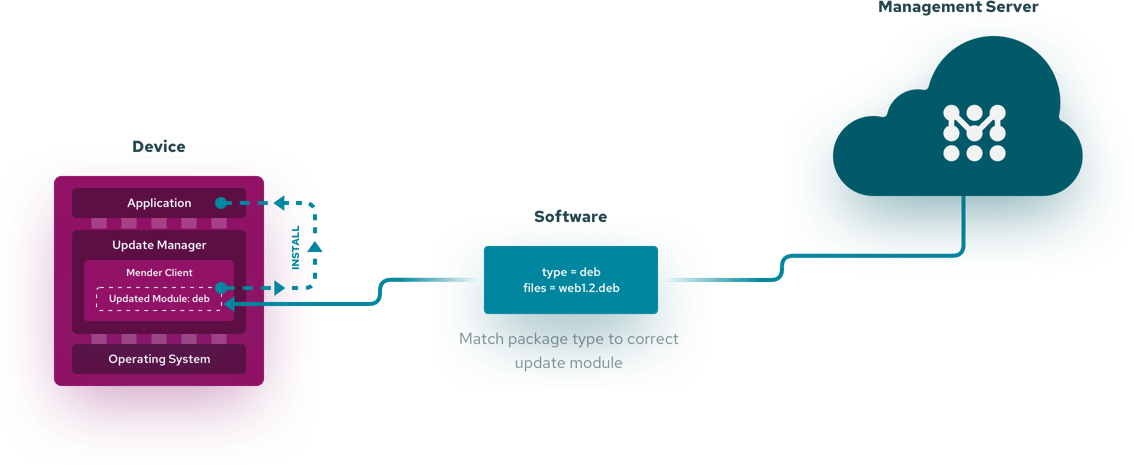
Installing the appropriate Update Module will enable support for installing different types of software packages, such as applications, containers, package managers, bootloaders, and proxy deployment for attached peripherals.
Tailor the Update Module to a specific device or environment, like updating a proprietary bootloader, or a generic use, like installing a set of packages. An existing Update Module can also be used as a starting point and adjusted to fit the exact update and environment requirements.
When the Mender Client downloads new software from the server, it will run the Update Module executable associated with the type of software downloaded. The Update Module is responsible for carrying out the steps needed to install the specified software. An Update Module can also support more advanced functionality, such as automatic rollback for an update failure.
Get started with Mender
Using Mender is easy! Get started quickly and deploy your first OTA update in minutes. Check out all the advanced Mender features free for up to 10 devices and 12 months.
Join the community
Mender is an open-source project with a great community. Join the discussion, explore tutorials, and find board integrations on our Mender Hub forum.
Technical FAQ
Check out the technical FAQs for more details about how Mender works, including compatibility, security, and scalability.