A powerful and state of the art processor is the backbone of every IoT project. NXP’s i.MX family of processors offer efficient power and graphics processing, and have become the industry standard for embedded designs.
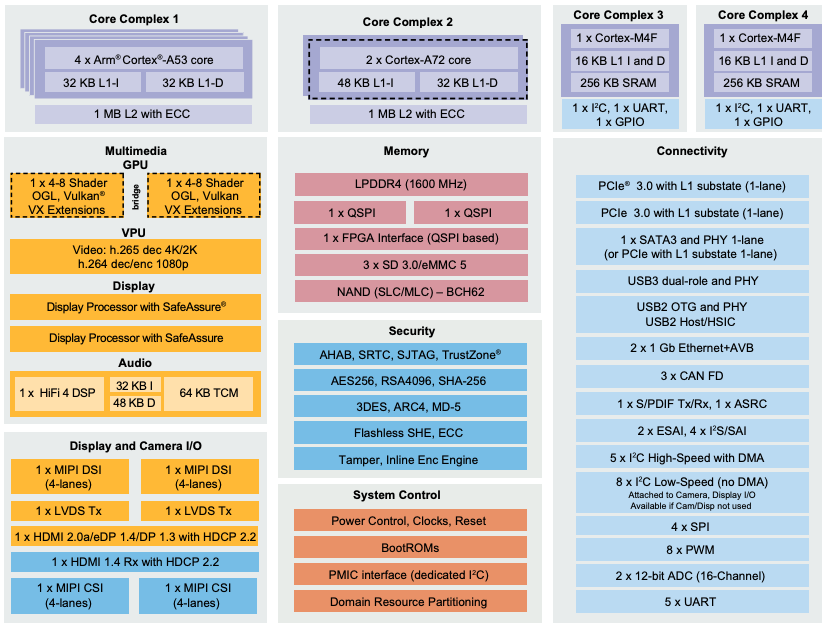
The i.MX 6 series are based on the ARM Cortex A9 solo, dual or quad cores (in some cases Cortex A7) and typically come with one or more Vivante GPUs. It is designed in CMOS 40 nm process. The i.MX 7 series is based on the low-power ARM Cortex A7 CPU core with a secondary ARM Cortex M4 real-time co-processor. It is designed in a 28 nm fully depleted silicon-on-insulator (FDSOI) process. The i.MX 8 series of applications processors is a highly scalable multicore platform that includes single-, dual- and quad-core families based on the Arm Cortex architecture including combined Cortex-A72 + Cortex-A53, Cortex-A35, Cortex-M4 and Cortex M7-based solutions for advanced graphics, imaging, machine vision, audio, voice, video and safety-critical applications.
Target applications for i.MX 8 series
The main target applications for the i.MX 8 series is automotive infotainment with instrument cluster, head unit, heads-up display (HUD), rear seat entertainment and full digital electronic cockpit; Advanced industrial human machine interface (HMI) and control, and system on modules and single board computers for home and industrial IoT applications.
Launched in 2017, the i.MX 8M series offers the following features:
- Up to four 1.5 GHz ARM Cortex-A53 processors
- Cortex-M4F for real-time processing
- LPDDR4, DDR4 and DDR3(L) memory support
- Two USB 3.0 interfaces with PHY and Type-C support
- Two PCIe interfaces (1-lane each) with L1 substates for fast wakeup and low power
- HDMI 2.0a and MIPI-DSI (4-lane) display interfaces • Up to two MIPI-CSI2 (4-lane) camera interfaces
- Gigabit Ethernet MAC with Audio Video Bridging (AVB) and EEE capability
- 4K UltraHD resolution and 10-bit High Dynamic Range (HDR) in H.264, H.265 and VP9 support
- Up to 4Kp60 resolution on the HDMI 2.0a output and 1080p60 resolution on the MIPI-DSI (4-lanes) interface
- OpenGL ES 3.1, OpenCL 1.2, OpenGL 3.0, OpenVG and Vulkan support
i.MX 8 family block architecture
Benefits of i.MX 8
There are number of key benefits to using an i.MX 8-based system in an embedded project: They can be summarised as follows:
Multiple platforms with multiple operating systems can be built on a single i.MX 8 processor. The i.MX 8 offers full-chip hardware-based virtualization, system MMU, resource partitioning and split GPU - a display architecture helps enable faster time to market and lower cost than simple hypervisor techniques alone.
Exceptional security is also assured via the SECO (security controller) with an isolated, dedicated hardware security module (HSM) protecting the system and its connections.
Critical services such as over-the-air (OTA) software upgrades can be isolated by running within 16 separate run-time programmable hardware firewall domains.
The i.MX 8 applications processor is built using 28nm FDSOI, which enables improved MTBF and decreases soft error rates due to FDSOI’s inherently high immunity to alpha particle flux.
Advanced vision-based human machine interface (HMI) systems can be created based on end-to-end vision processing which helps enable vision-based assistance, tracking and object detection.
360-degree expanded sight Utilize multi-camera input, digital stitching and VX vision extensions and provide a view from any angle.
Multi-domain voice recognition Utilize the Arm Cortex-A72, Cortex A53 and CortexM4F cores as well as the HiFi 4 DSP for advanced echo cancellation, key word detection and speech recognition for hands-off interaction.
Multi-screen platforms can be developed through the ability to drive up to four 1080p screens with independent content, or a single 4K screen.
i.MX embedded SOM and the Yocto Project
NXP provides documentation on how to build an image for an i.MX-based embedded SOM by using a Yocto Project build environment. It describes the i.MX release layer and i.MX-specific usage. On the Mender Hub, there is also a tutorial on how to integrate a SOM based on the i.MX 8 M Mini with Mender and Yocto.
i.MX embedded SOM and secure OTA updates
In this recorded webinar Drew Moseley, Embedded Linux Engineer, and Rudan Bettelheim, Product Manager, NXP, describe the implementation of a secure and robust OTA software update manager using Mender for an i.MX 8MQuad-based embedded SOM. Mender partner and embedded design studio Embedded Artists have also created a short video tutorial to guide you through the process of setting up OTA software updates for an i.MX 8 based SOM.
NXP has developed an implementation for secure OTA software updates for Linux images for the i.MX 8M/MM families using Cryptographic Acceleration and Assurance Module (CAAM) accelerator and Mender. Its purpose is to perform U-Boot, rootfs, and software application updates.
Recent articles
New Mender experimental AI-enabled feature
Mender in 2025: A year in review with compliance, security, and AI-driven growth
What’s new in Mender: Enhanced delta updates and user experience
Learn why leading companies choose Mender
Discover how Mender empowers both you and your customers with secure and reliable over-the-air updates for IoT devices. Focus on your product, and benefit from specialized OTA expertise and best practices.