OTA Update for Embedded Linux Systems

Operating systems (OS) based on Linux are used in many embedded system architectures. Embedded Linux systems are very popular platforms for development and production of internet connected embedded devices, also referred to as the Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices.
In embedded Linux device development, there are two approaches when it comes to what operating system to run your device on. You either build your own distribution such as Yocto, Buildroot, or you use a binary distribution such as Debian, Ubuntu, and Raspbian.
There are many reasons that have contributed to the adoption of Linux including having an open source community, the support for necessary functionality such as WiFi, Bluetooth and so on. Linux has also been ported to a wide range of processor architectures commonly found in SoC designs such as x86, MIPS and ARM.
When it comes to an update mechanism for updating the software on these embedded connected devices in the field there are few options available. The most efficient mechanism is over-the-air (OTA) update where the update is sent and managed remotely without any requirement for physical or manual (at-the-device) input. For this to occur, a central server to control the update process is necessary with the software client installed on the device. The software client is responsible for executing the update on the device based on the commands of the server.
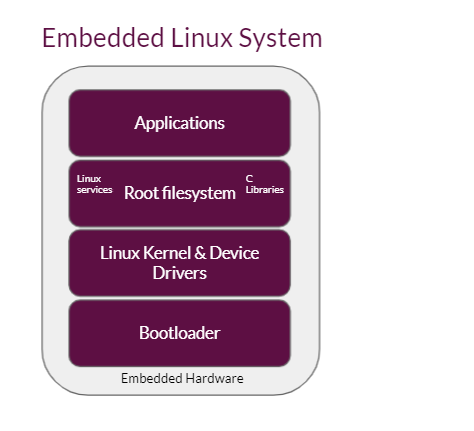
Embedded connected devices running on Linux are varied in their design and implementation but the common components required for deploying OTA software updates are the bootloader, kernel, root filesystem on the root partition and any other software existing on other partitions of the device.
Updating software could appear an easy task in the initial stages of product planning but the development team could fail to realize the many intricacies of a system that is susceptible to the environment that an IoT device in the field functions. What if something goes down such as the power or network during an update, what if a bug renders a portion of the device unbootable, what if a malicious software is sent to device, and so on.
Using Mender for OTA updates
Mender provides flexibility in choosing your infrastructure (hosted or on-prem), software, and hardware (custom built such as in Yocto) and binary (such as in Raspberry Pi) from prototyping to production. Server operations are available through an public API which means there is no vendor lock-in.
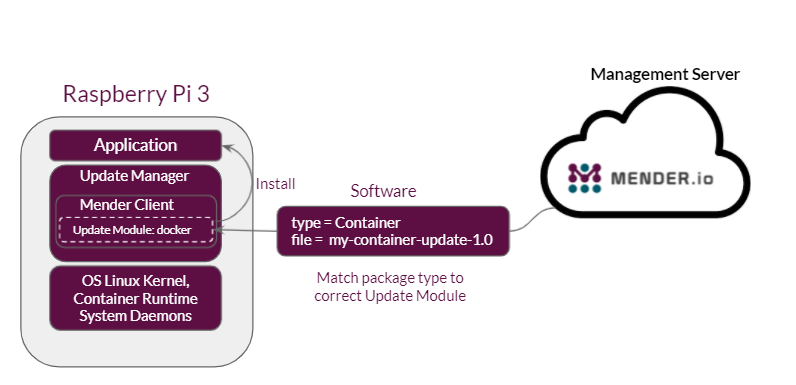
Mender supports both system and application software updates in embedded Linux OTA updates. Many in the industry refer to system updates as firmware updates or firmware over-the-air (FOTA). This is usually the bootloader, kernel, and root filesystems. Application or software over-the-air (SOTA) update refers to software in the user space that could be containers, packages, files and directories.
Mender performs application updates using Update Module which allows for different types of software to be installed on the device. Mender also provides the freedom to do a custom update by employing state scripts.
Mender’s prime directive in deploying OTA software updates is security and robustness. Secure to prevent the device from being hijacked by attackers installing unauthorized software and robust so that an update does not make the device unusable. It ensures there is a fall-back mode if something fails such as power or network connectivity and that there are no half-done software installations (atomicity).
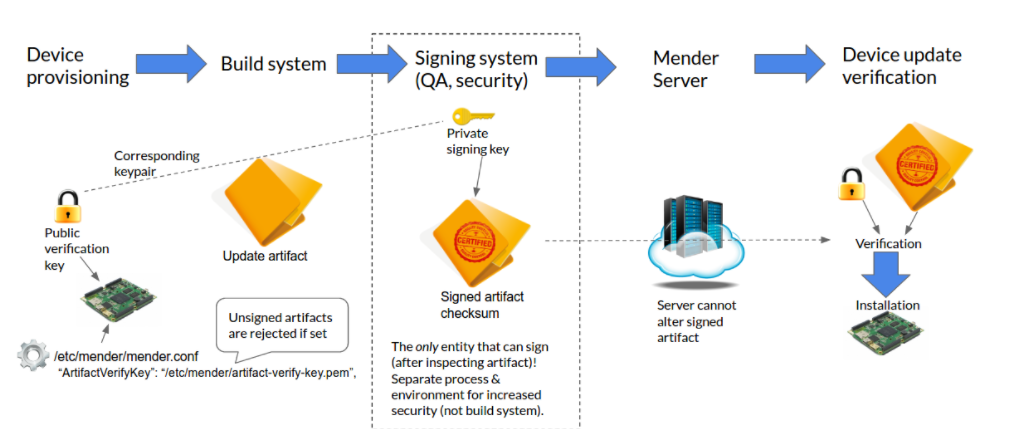
An important part of security and robustness is to give the ability to verify that the updates come from a trusted source. Mender achieves this by signing the Artifact (software files) using a protected private key which is stored and used in a signing system. The Mender client running on the device verifies it using the corresponding public key. If this signature verification passes then the update is considered trustworthy and proceeds for installation. The below diagram shows the high level flow of creating and managing keys and Artifact signatures.
Get started with Mender
You can quickly and easily deploy an OTA update with Mender using a secure server hosted for you. Follow this step-by-step guide to do simple application, system and container updates with a Raspberry Pi.
Mender is free to try for up to 12 months — no credit card is required. Start today and connect up to 10 devices for free! Sign up here.
Recent articles
Complying with the US FDA and EU MDR requires software updates
IoT in 2026: Edge AI, growing complexity, and the demand for smarter updates
New Mender experimental AI-enabled feature
Learn why leading companies choose Mender
Discover how Mender empowers both you and your customers with secure and reliable over-the-air updates for IoT devices. Focus on your product, and benefit from specialized OTA expertise and best practices.