Top Trend #3: Reduce operational costs and realize the business value of IoT with delta updates


Industrial operations, building management systems, or consumer vehicles — to acquire data from connected assets, organizations must invest in a best-of-breed over-the-air (OTA) update solution within its embedded device strategy. As connected assets are often geographically dispersed or exist in remote locations, their operation depends on cellular or satellite data networks. Any data transfer to or from these devices occurs over the air.
Importantly, the requirement to transfer data incurs a significant operational cost as device fleets scale and the size and complexity of the deployed software update images increase. There is a strategic way to control these costs while increasing the business and customer value that can be extracted from the connected device fleet.
Enter Delta Updates
For updating software over the air, binary deltas enable bandwidth cost savings for metered networks, such as cellular (i.e., 4G/LTE) or satellite. This key strategic lever offers the ability to generate and only deploy the binary difference (delta) between the software version already on the devices and the new version. When coupled with a robust and atomic rollback approach, this OTA method also ensures the device is never ‘bricked’ or rendered unusable. These deltas can also be auto-generated on the management server side to better manage the update process at scale.
When a product management or machine data platform team is assembling its internal business case for an investment in a professional OTA update manager, projecting the future cost of mobile plans as the connected device fleet scales can be helpful to secure funding. Teams can do this by projecting and demonstrating the cost savings realized from applying delta OTA updates to remote machinery as the connected device fleet grows over a multi-year period. Both corporate and the supported business unit will be better able to understand why they should pay for the device fleet management service. The business can generate new value from OTA updates by offering new software services to customers and capturing machine data for analysis and reuse without increasing mobile plan costs to unsustainable levels.
Example 1: Canonical study on bandwidth savings from applying a delta update strategy
Several providers have researched the bandwidth savings organizations can realize from using delta (differential) updates to control operational costs. For instance, Canonical investigated how its snap delta updates technology for the Ubuntu OS was helping customers realize significant bandwidth savings in managing their IoT device fleets. Canonical’s research team compared the ratio of delta versus full download sizes and the time spent applying the delta on a configuration typically found on IoT devices. The team looked at the use of delta updates on Dell Edge Gateways and found that bandwidth consumption was reduced by 60.51% for Dell Edge 3000-series devices.
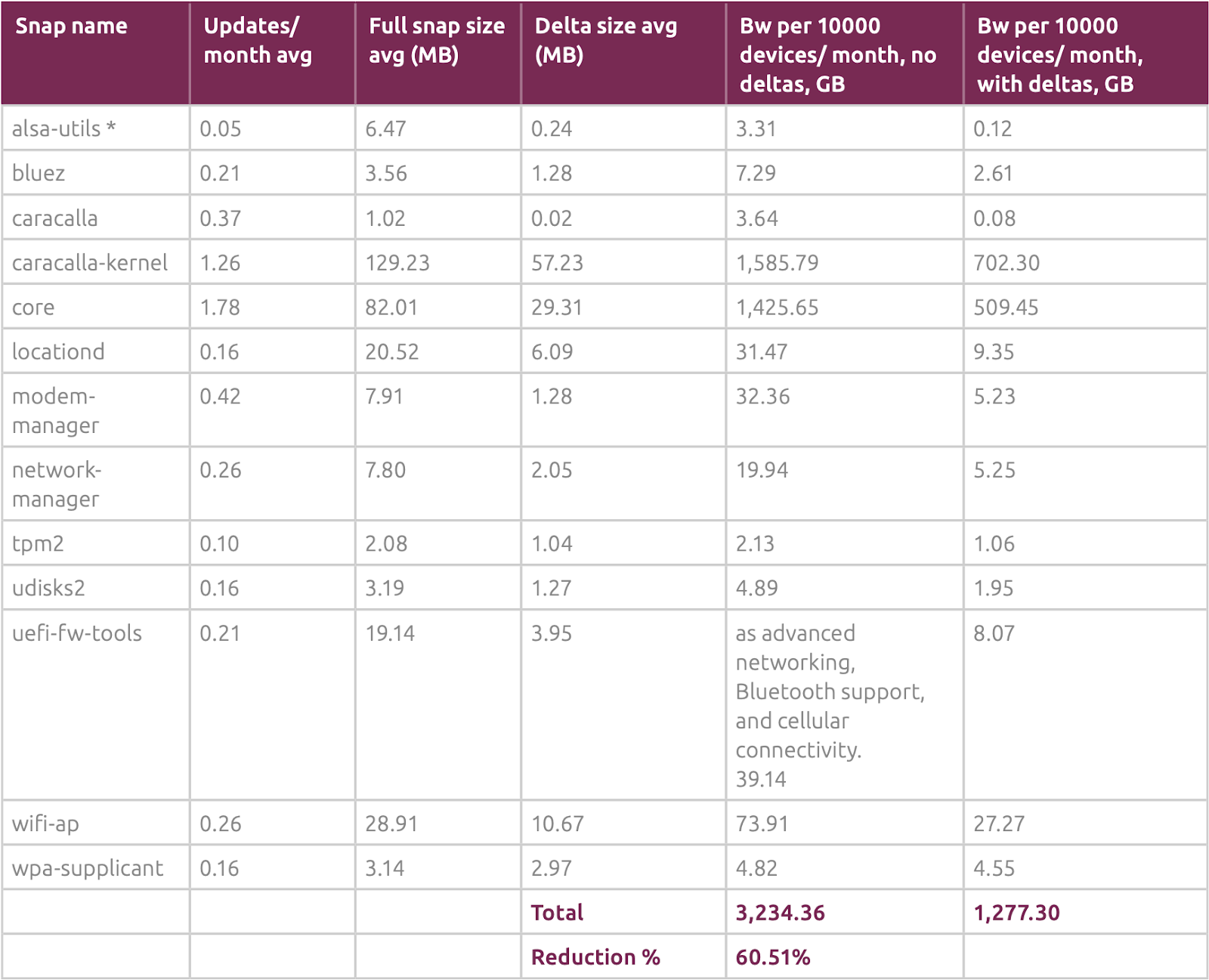 Caption: Credit: Canonical: How delta updates on Dell Edge Gateways reduced bandwidth consumption by 60.51% for Dell Edge 3000-series devices.
Caption: Credit: Canonical: How delta updates on Dell Edge Gateways reduced bandwidth consumption by 60.51% for Dell Edge 3000-series devices.
Rigado’s Cascade 500 IoT Gateway and edge application platform users using snap deltas reduced bandwidth usage by 65.43%.
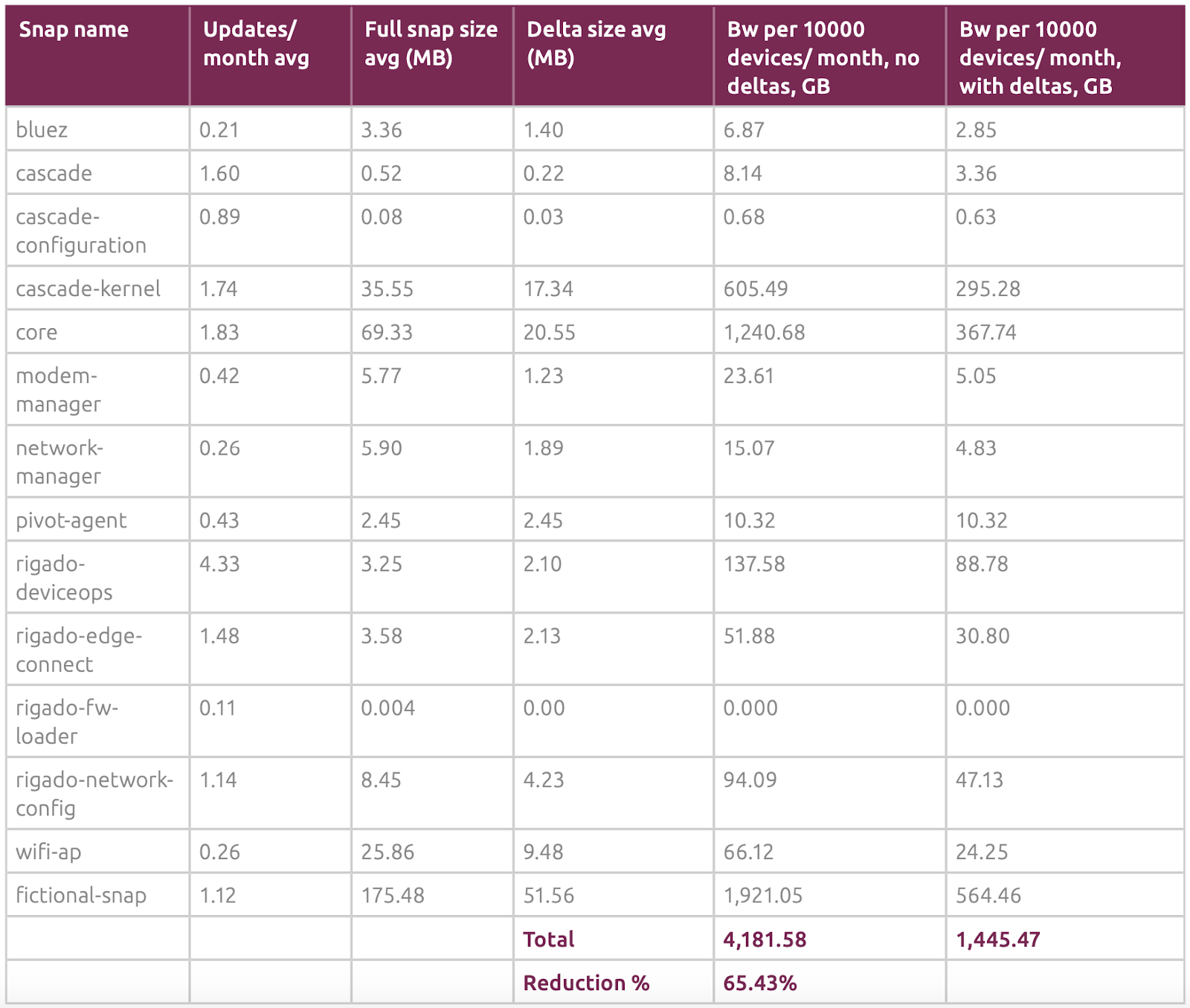 Caption: Credit: Canonical: How the use of delta updates on Rigado’s Cascade 500 IoT Gateway and edge application platform reduced bandwidth usage by 65.43%
Caption: Credit: Canonical: How the use of delta updates on Rigado’s Cascade 500 IoT Gateway and edge application platform reduced bandwidth usage by 65.43%
Example 2: Modeling cost savings from applying a delta update strategy
The Northern.tech engineering team published research on the business value of delta updates in an OTA update management system.
To illustrate the cost savings, the team researched the data transfer cost over a typical mobile network, discovering mobile data costs vary significantly across countries worldwide. After research on an extensive analysis of mobile data pricing across the globe, the team found an average cost of $12.37 for 1 GB of data in the United States.
The team then modeled the cost savings of delta updates based on the assumption that an existing OS image is 239 MB (after compression) with a new update package that adds 30 MB to the total size. With delta updates, only approximately 30 MB is downloaded instead of the 269 MB actual full image. The 30 MB does not necessarily mean an increase in the image size; rather, only 30 MB of the image changed and is being deployed over the air. These results translated to significant cost and performance differentials – expected faster download times with the smaller file size or lower data costs. The average cost savings for one device and one update is an 89% reduction versus a full image update. With deployments to one thousand devices requiring four updates per year, the model projects cellular costs of $1,484 for delta updates compared to $13,310 for full image updates.
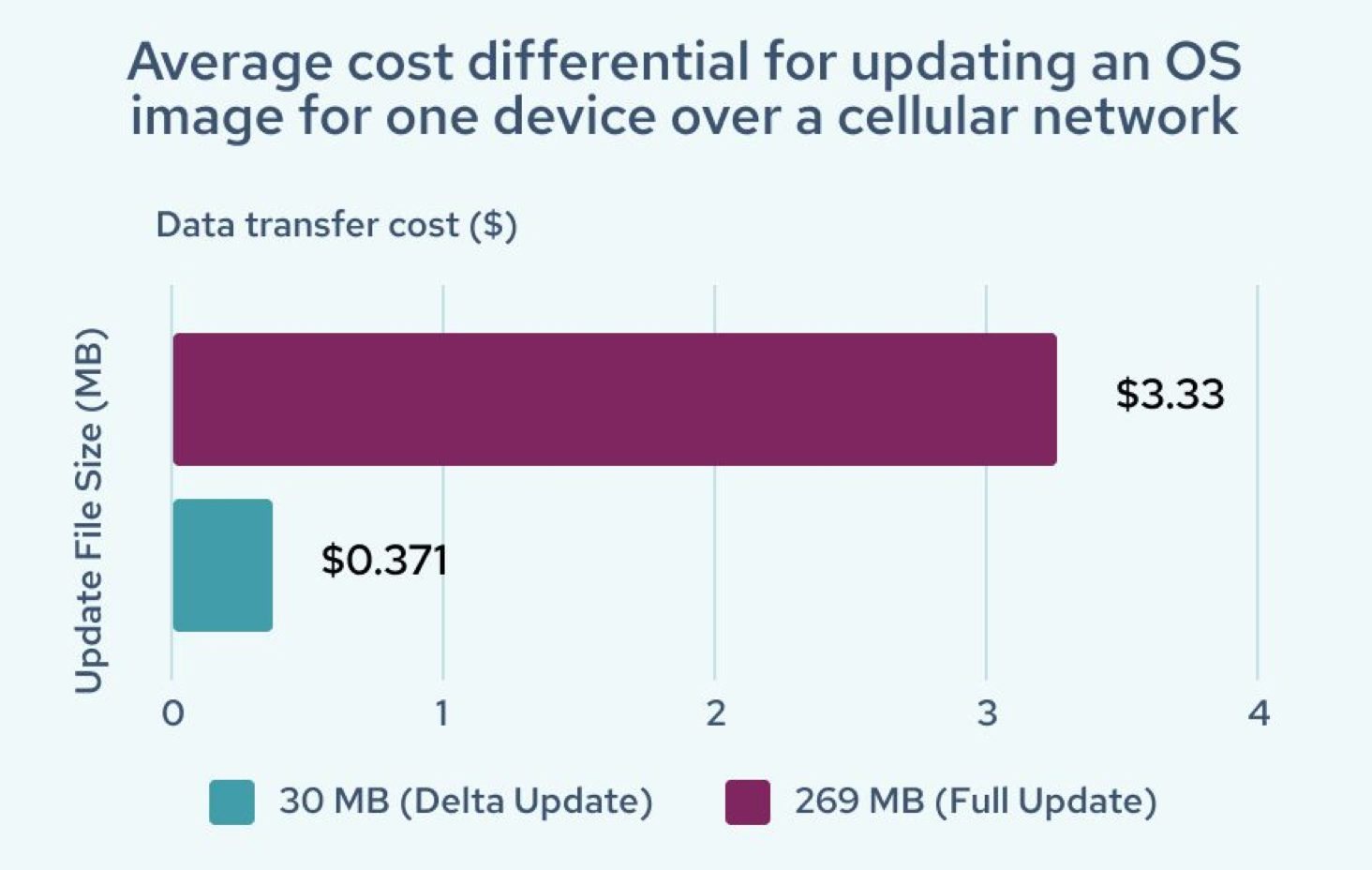 Caption: Importance of a Scalable IoT Infrastructure for Device Management white paper demonstrates significant cost savings from using OTA delta updates.
Caption: Importance of a Scalable IoT Infrastructure for Device Management white paper demonstrates significant cost savings from using OTA delta updates.
Leveraging Delta Updates for Greater Control
Delta updates are an essential component of a best-of-breed OTA update manager. The evidence of bandwidth and cost savings make a case for controlling the cost of a scaling device fleet while realizing the value from connected devices, new digital services, and machine data capture for the business.
Try out Delta Updates in the Mender enterprise trial
- Sign up for your free trial
- Explore delta updates in our tech docs
Recent articles
New Mender experimental AI-enabled feature
Mender in 2025: A year in review with compliance, security, and AI-driven growth
What’s new in Mender: Enhanced delta updates and user experience
Learn why leading companies choose Mender
Discover how Mender empowers both you and your customers with secure and reliable over-the-air updates for IoT devices. Focus on your product, and benefit from specialized OTA expertise and best practices.